The brain is undeniably the most important and powerful organ in our body, but also highly vulnerable to injury and disease. A blood clot in your brain is a serious health condition, "that can lead to stroke or even death," Dr. Tomi Mitchell, a Board-Certified Family Physician with Holistic Wellness Strategies tells us. "While prompt medical treatment is essential, it can be challenging to identify the symptoms of a brain clot. However, four key signs may indicate that you have a clot in your brain."
Blood Clots in the Brain are Common and Anyone is at Risk

Dr. Mitchell tells us, "While they can occur in anyone at any age, they are most common in older adults. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, around 795,000 Americans suffer from a stroke each year, and a blood clot causes about 87% of those. While most people recover from a stroke, some have long-term disabilities. However, the risk of suffering a stroke increases with age, so it's essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms."
What Causes a Blood Clot in the Brain?
According to Dr. Mitchell, "It occurs when a blood vessel in the brain becomes blocked, usually by plaque buildup. This can happen either suddenly, as in the case of a traumatic injury, or gradually over time. If the clot is not treated quickly, it can cause permanent damage to the brain tissue. Several risk factors for developing a blood clot in the brain include high blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking. Treatment typically involves taking medication to thin the blood and dissolve the clot. In some cases, surgery may also be necessary. The best way to prevent a blood clot in the brain is to live a healthy lifestyle and manage any underlying medical conditions."
Serious Health Complications Can Happen as a Result of a Brain Blood Clot
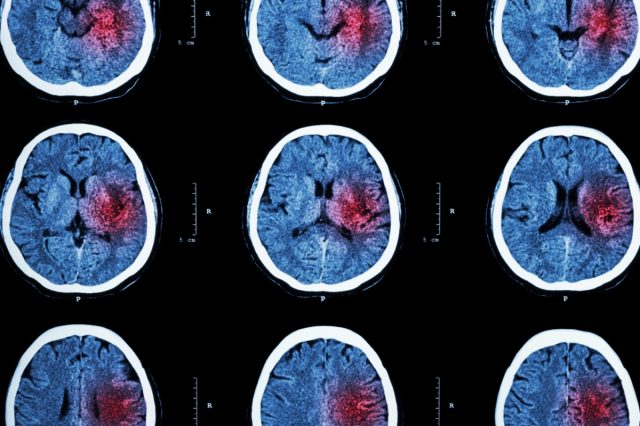
Dr. Mitchell explains, "If a blood clot forms in your brain, it can cause a stroke. A stroke occurs when the blood flow to your brain is cut off, leading to paralysis, problems with speech and vision, and even death. A blood clot in your brain can also cause a transient ischemic attack (TIA), often called a "mini-stroke." Although a TIA doesn't last as long as a stroke, it's still a severe condition and can be a warning sign that you're at risk of having a stroke in the future. If you have any symptoms of a TIA or stroke, you should seek medical help immediately."
Brain Blood Clot Diagnosis and Treatment

Dr. Mitchell shares, "While diagnosing a blood clot using a CT scan or MRI is often possible, the most definitive way to confirm the diagnosis is through an angiogram. During an angiogram, a thin tube is inserted into an artery in the arm and threaded through the body to the brain. Once in place, a dye is injected into the street, which allows the doctor to see any blockages on the X-ray. If a blood clot is found, there are two main ways to treat it. The first option is to insert a small device called a stent that can help to open up the blocked artery. The second option is surgery to remove the clot. Regardless of the chosen treatment, acting quickly to minimize the risk of serious complications is essential."
Sudden Onset of Severe Headache
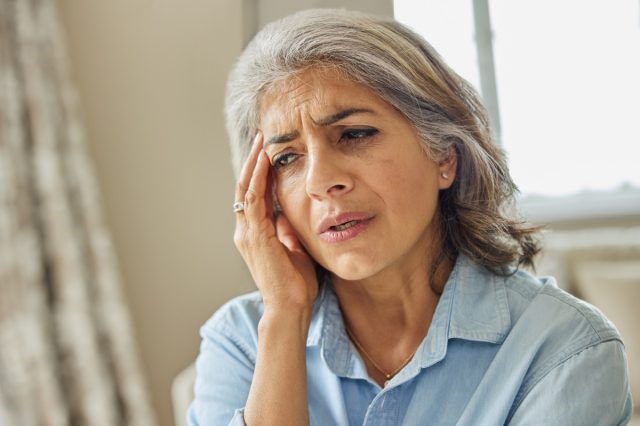

Dr. Mitchell says, "A severe headache is often one of the first signs that you might have a clot in your brain. Clots can occur when there is an injury to the blood vessels in the brain or if a buildup of plaque narrows the arteries and cuts off blood flow. When this happens, oxygen and nutrients cannot reach the brain tissue, leading to cell death. In addition, clots can cause bleeding in the brain, which can lead to further damage. While not all headaches indicate a clot, the sudden onset of a severe headache is a sign that you should seek medical attention immediately. If left untreated, clots can cause permanent damage to the brain or even death."
Nausea and Vomiting

"Sudden onset nausea and vomiting can signify a clot in your brain for a few reasons," states Dr. Mitchell. "First, if the clot is large enough, it can cause increased pressure on the surrounding brain tissue, leading to nausea and vomiting. Additionally, clots can disrupt the normal flow of blood and cerebrospinal fluid within the brain, causing congestion and irritation that can also lead to these symptoms. Finally, some clotting disorders may cause an imbalance in the levels of hormones involved in nausea and vomiting, resulting in sudden onset of nausea and vomiting even in the absence of other symptoms. If you experience these symptoms, seeking medical attention as soon as possible is essential to rule out a potentially life-threatening condition."
Speech Problems
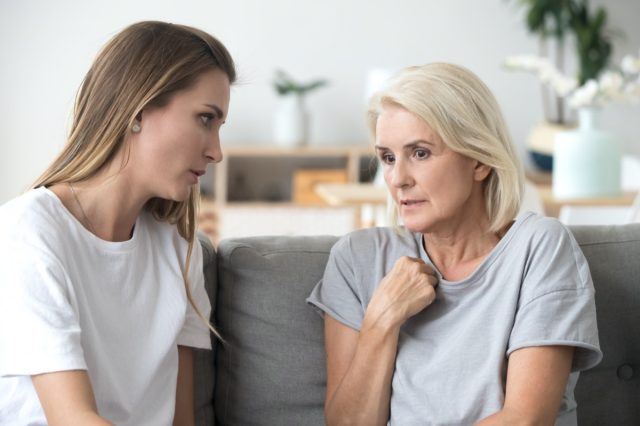

Dr. Mitchell explains, "A clot in an artery that supplies blood to the brain can cause a sudden onset of speech problems. This is because the clot can block or restrict blood flow to the brain's area that controls language. Without a steady supply of oxygen-rich blood, nerve cells in the affected area can become damaged or die. Sometimes, a clot may only partially block an artery, leading to temporary speech problems. However, if a clot completely blocks an artery, it can cause a stroke, resulting in permanent brain damage."
Loss of Balance
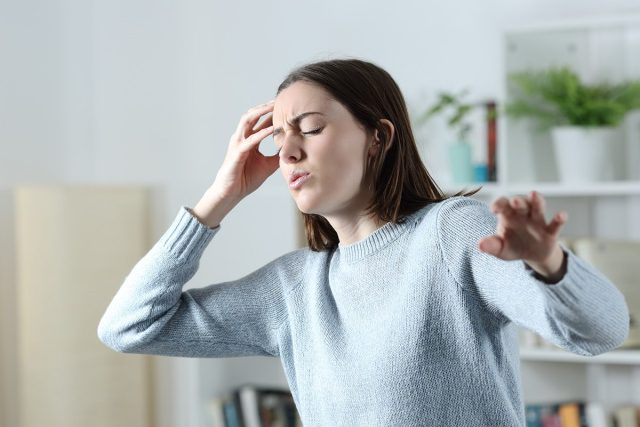

"A brain clot can cause dizziness and loss of balance, making it difficult to walk or stand," says Dr. Mitchell. "Sudden loss of balance can signify that you might have a clot in your brain. When a clot forms in an artery in the brain, it can block blood flow to the brain and cause a stroke. Clots can also develop in veins, the blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart. If a clot forms in a vein, it is called venous thrombosis. Venous thrombosis can also block blood flow to the brain and cause a stroke. The sudden loss of balance is caused by the lack of blood flow to the brain. When you lose balance, you may fall and hit your head, which can cause additional damage to the brain."
Time Isn't On Your Side

Dr. Mitchell emphasizes, "When it comes to stroke detection, time is of the essence. Medical professionals use the FAST mnemonic – Face, Arms, Speech, Time. By quickly assessing these four key signs, they can determine whether someone is having a stroke and get them the treatment they need as soon as possible.
Face: Is one side of the face drooping? Does the smile look uneven?
Arms: Is one arm weak or numb? Raise both arms and see if one drifts down.
Speech: Is speech slurred or garbled? Can the person repeat a simple sentence?
Time: If any of these signs are present, it's time to call 911.
Even if the symptoms go away, it's essential to get checked out by a medical professional as soon as possible. With prompt treatment, many of the effects of a stroke can be reversed. So don't wait – make the call now."
Adi Iyer, MD, neurosurgeon, of Pacific Neuroscience Institute at Providence Saint John's Health Center in Santa Monica, CA adds, "Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States and a major cause of serious long-term disability. Some signs of having a stroke include weakness or numbness on one side of the body, a drooping face, difficulty finding words or understanding language and full or partial loss of vision. This indicates that a critical region of the brain responsible for that function is not getting oxygen. This is most commonly from a clot that is blocking blood from flowing through the major brain artery. For example numbness, weakness and facial drooping occur when the blood vessel going to the sensorimotor region of the brain is blocked. Vision loss occurs when the artery going to the retina is blocked.
Dr. Mitchell says this "doesn't constitute medical advice and by no means are these answers meant to be comprehensive. Rather, it's to encourage discussions about health choices."
No comments:
Post a Comment