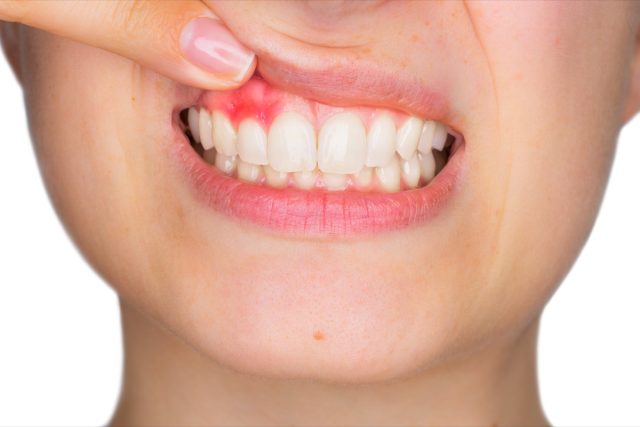
The type of inflammation caused by excess weight has been associated with numerous health risks, including development of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular issues. Now, new research suggests there may be one risk you may not have considered: gum disease.
A study in the Journal of Dental Research found that excessive inflammation linked to obesity increased the amount of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, or MDSCs. These originate in bone marrow and develop into numerous cell types, including a kind called osteoclasts that break down bone tissue.
That's an issue throughout the body, but can be particularly problematic in your mouth, the researchers note. That's because bone holds your teeth in place, and when that foundation is weakened, it can lead to gum disease and potential tooth loss.
"Previous research suggests there's a clear relationship between obesity and gum disease and our study shows that might be due to higher amounts of osteoclasts," says study co-author Keith Kirkwood, DDS, Ph.D., professor of oral biology at the University of Buffalo School of Dental Medicine.
Although the study examined two groups of mice—with one group fed a diet that caused fast weight gain and subsequent inflammation spikes—the results are likely similar in people since the mechanism is the same, says Kirkwood.
"This process would not only explain the connection between excess weight and gum disease, but may also shed light on mechanisms behind other inflammatory, bone-related diseases that tend to develop along with obesity," he adds. That includes arthritis and osteoporosis.
Why does weight gain cause such a dramatic reaction? Some experts have noted that overeating can increase the immune response because the body is stressed by that level of consumption.
In response, the immune system generates excessive inflammation as a way to handle the threat. If you overeat occasionally, that's not a big deal, because your inflammation will lower once the perceived stress has passed. But, regularly consuming high amounts, and gaining weight as a result, will make that inflammation chronic, and that's when the health risks begin increasing.
"It's a balancing act," says Bente Halvorsen, Ph.D., professor at the Research Institute for Internal Medicine at the University of Oslo in Norway. "But we can reduce the inflammatory reaction by losing weight, or at least by being more conscious of the effects of gaining weight."
No comments:
Post a Comment